Phase envelopes
Two-phase envelopes
Two-phase envelopes show all the saturation points of a mixture, they can be seen as the boundary line of transition between monophasic regions to two-phase equilibria regions.
In yaeos it is possible to calculate two-phase of different kinds.
- Isoplets
Isoplets
Isoplets are the phase boundaries at constant composition (the global composition) of the system. Here is a simple example with commentaries on how a phase boundary can be calculated:
program phase_diagram
!! Program for calculation of phase diagrams.
use forsus, only: Substance, forsus_dir, forsus_default_dir
use yaeos, only: pr, &
SoaveRedlichKwong, PengRobinson76, PengRobinson78, RKPR, &
EquilibriaState, ArModel, PTEnvel2, &
pt_envelope_2ph, saturation_pressure, saturation_temperature
use yaeos__phase_equilibria_auxiliar, only: k_wilson
implicit none
! ===========================================================================
! Variables definition
! ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
integer, parameter :: nc=2
class(ArModel), allocatable :: model ! Thermodynamic model to be used
type(EquilibriaState) :: sat_point ! Init
type(PTEnvel2) :: envelope ! PT Phase envelope
real(pr) :: tc(nc), pc(nc), w(nc) ! Component's critical constants
real(pr) :: n(nc) ! Termodynamic variables
type(Substance) :: sus(nc) ! Substances to use
! ===========================================================================
! forsus database directory
forsus_dir = "build/dependencies/forsus/" // forsus_default_dir
! Find the selected substances on the database and extract their
! critical constants
sus(1) = Substance("methane")
sus(2) = Substance("n-hexane")
call get_critical_constants(sus, tc, pc, w)
! Model definition
model = PengRobinson76(tc, pc, w)
! Composition vector
n = [0.9_pr, 0.1_pr]
! Calculate a dew point at low pressure to later
! initialize the phase envelope
sat_point = saturation_temperature(model, n, P=1._pr, kind="dew", t0=150._pr)
! Calculate phase envelope
envelope = pt_envelope_2ph(model, n, sat_point)
! Write the phase envelope to screen
write(*, *) envelope
contains
subroutine get_critical_constants(subs, tc_in, pc_in, w_in)
type(Substance) :: subs(:)
real(pr), intent(out) :: tc_in(:), pc_in(:), w_in(:)
tc_in = subs%critical%critical_temperature%value
pc_in = subs%critical%critical_pressure%value/1e5
w_in = subs%critical%acentric_factor%value
end subroutine
end program phase_diagram
The output of the write command will be pre-formatted. Showing in tabular
data with this
# PTEnvel2
# kind of sat point
kind T P [liquid-phase composition vector] [gas-phase composition vector]
# other kind of sat point
kind T P [liquid-phase composition vector] [gas-phase composition vector]
# Critical
T P
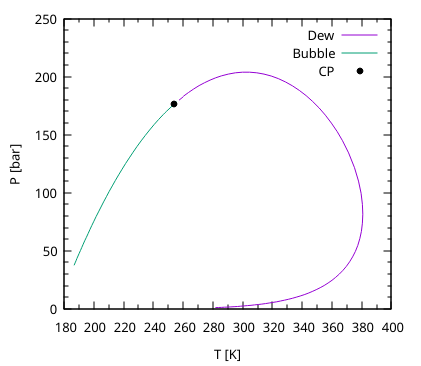
Which when plotted with gnuplot with:
plot "outfile" \
index "dew" u 2:3 w l title "Dew", \
"" index "bubble" u 2:3 w l t "Bubble", \
"" index "Critical" u 1:2 w p pt 7 lc rgb "black" t "CP"
Gives the following plot: